The term “cancer” refers to the abnormal growth of cells and usually stems from a single abnormal cell. Due to the loss of standard control mechanisms, cells are capable of multiplying and invading nearby tissues, sometimes far from the original site of infection (metastasis). Thus they form blood vessels from which they obtain nutrients. Cancer (malignant) cells can develop from any tissue. Hence there are various types of cancer.
The growth and multiplication of cancer cells form a mass of cancerous tissue called a tumor. It invades and destroys the surrounding normal tissue. Tumors are abnormal masses and may or may not be cancerous.
Let’s learn a little more about this serious condition here.
Types of cancer
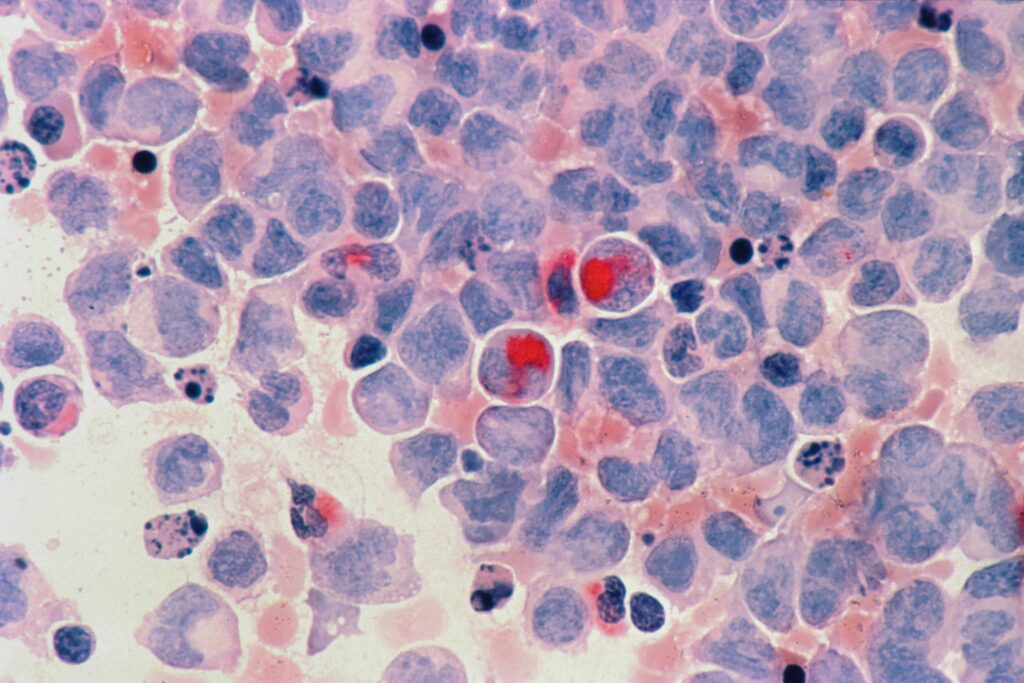
There are two types of cancer tissue: those that form in the blood, hematopoietic cells (leukemias and lymphomas), and those that form as solid masses (solid tumors).
Solid tumors that are cancerous can be classified as carcinomas or sarcomas. Additional classifications can be made based on the organ in which cancer develops and the type of cell that contains it.
There are two types of cancer, leukemia, and lymphoma, those that affect the blood and blood-forming tissues, and those that affect the immune system.
Blood-forming cells in the bone marrow cause leukemias, which crowd out normal cells.
Lymph node expansion by lymphomas can cause large masses in the armpits, groin, abdomen, and chest.
What can affect cancer?
It is a disease that affects the cells lining the skin, lungs, digestive tract, and internal organs.
Carcinomas include skin cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, stomach cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and thyroid cancer.
In general, it is more common for older people to develop carcinomas than younger ones.
Sarcomas are a cancer of the mesodermal cells. Connective tissues, muscles, blood vessels, and bones are made up of mesodermal cells. Sarcomas include leiomyosarcomas (cancers of the smooth muscle found in the walls of the digestive organs) and osteosarcomas (cancers of the bone).
Younger people tend to be more likely to develop sarcomas than older people.
How to define cancer?
Neoplasia is defined as a tumor, whether cancerous or non-cancerous. Then, malignant transformation is a complex process by which cancer cells develop from healthy cells.
According to its stage, to the extent that cancer has spread, we can know the degree of abnormality in the appearance of the cancer cells. Through microscopic examination, it is seen that the most abnormal-appearing cells are more aggressive
Through invasion, cancer can grow and destroy surrounding tissue or spread to an entirely new location.
Even after treatment, there can be a recurrence, when cancer cells come back after treatment, either in the primary location or as metastases.
Or, if all goes well, there may be a remission, the absence of any evidence of cancer after treatment, even though there may still be cancer in the body. This determines a survival rate, the percentage of people who survive for a period of time after treatment.
The aggression of a tumor

This is determined by the shape and speed at which it grows and spreads.
Malignant: Cancer cells invade nearby tissue and can spread to other parts of the body.
Benign: not cancerous. The bloodstream or lymphatic system does not transport or spread benign tumors to distant sites. However, it is still possible for benign tumors to grow, press on neighboring tissues and cause problems.
A carcinogen is a substance that causes cancer.
Carcinoma in situ: Cancer cells that have not yet invaded surrounding normal tissue or spread to other parts of the body, but are still growing in the tissue where they started. Its effective cure is based on the complete elimination of cancer so that it does not reappear.
To the extent that cancer cells have matured, stopped dividing, and assumed normal cellular functions. So they are no longer seen as primitive cells that multiply rapidly.
Cancer risk factors
A number of genetic and environmental factors increase the risk of developing cancer. It is important to recognize that not everyone who is exposed to carcinogens or who has other risk factors develops cancer.
family history
The risk of developing certain types of cancer is significantly higher in some families. In some cases, this risk is determined by a gene, and in other cases, it is the result of the interaction of several genes. This genetic interaction can be altered by environmental factors common to the family.
genes and chromosomes
Cancer is believed to be caused by abnormalities (mutations) affecting critical genes. A protein produced by these genes regulates growth, alters cell division, and affects basic cell properties.
It is possible to develop cancer if you have an extra or abnormal chromosome. People with Down syndrome are at increased risk of acute leukemia and carcinoma.
Several factors can cause genetic mutations that lead to cancers: chemicals, sunlight, medications, viruses, and other environmental factors. There are families in which these abnormal cancer-causing genes are passed down from generation to generation.
Genes associated with cancer fall into two categories: oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.
An oncogene is a mutated or amplified form of a gene that normally regulates cell growth. Some forms of lung cancer are caused by the EGFR and HER2 oncogenes.
As a result of inappropriate signaling, some oncogenes promote uncontrolled cell division, leading to cancer. Oncogenes are produced when normal genes are mutated, but many factors may be involved, including:
- X-rays
- Sunlight
- Toxins at work, in the air, or in chemicals (such as cigarette smoke)
- Infectious agents and certain viruses
Tumor suppressor genes regulate the growth of cancer cells by coding for proteins that repair damaged DNA. Cancer risk increases when DNA damage prevents tumor suppressor genes from working, allowing affected cells to multiply indefinitely.
A certain percentage of breast cancer is caused by suppressor gene mutations, typically inherited from the parents.
Age and types of cancer

Several types of cancer occur almost exclusively in children: Wilms tumors, retinoblastomas, and neuroblastomas.
Mutations in suppressor genes cause these cancers, either by inheritance or during fetal development.
Adults are more likely to get most other types of cancer, especially those that occur in older adults. In addition to increased exposure to carcinogens, the body’s immune system has been weakened.
Environmental factors
A number of environmental factors increase the risk of developing various types of cancer.
Inhalation of tobacco smoke can cause cancer of the lungs, mouth, throat, esophagus, kidneys, and bladder due to its carcinogenic content.
Cancer can be caused by air or water pollution, such as asbestos or industrial waste.
Many chemicals are known to cause cancer, and many more are suspected of causing it. Asbestos exposure can cause lung and pleural cancer. Some types of cancer (leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma) are associated with pesticide exposure.
It can take many years for a person to develop cancer after being exposed to chemicals.
radiation exposure
Mainly sunlight causes skin cancers when exposed to ultraviolet radiation for a long period of time.
Ionizing radiation from x-rays is carcinogenic. People with many tests have a slightly higher risk of cancer.
As a result of exposure to the radioactive gas radon, which comes from the ground, the risks of lung cancer are increased. Radon can accumulate inside a building when it is built on radon-containing soil, reaching harmful levels in the air and can lead to lung cancer. Smokers exposed to this risk have an even higher risk of lung cancer.
It is necessary to determine which other chemicals increase the risk of cancer among many other substances.
Geography
Although the reasons for geographic differences in cancer risk are complex and poorly understood, the risk of various types of cancer varies depending on where people live.
The risks are likely multifactorial: a combination of genetics, diet, and environment.
There are some viruses that cause cancer only in certain countries. The Epstein-Barr virus, for example, causes Burkitt’s lymphoma (a form of cancer) in Africa and cancer of the nose and pharynx in Asia.
Diet
Cancer risks may be increased by substances related to the diet. Saturated fat in the diet, as well as obesity, have been linked to an increased risk of colon, breast, and prostate cancer.
The risk of liver cancer, head, and neck cancer, and esophageal cancer is significantly higher for those who drink excessive amounts of alcohol.
Illnesses caused by smoked and pickled foods or grilled meats are more likely to occur when you eat these foods frequently. People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop cancer of the breast, endometrium, colon, kidney, and esophagus.
Medicines and medical treatments
Certain medications and treatments can increase the risk of developing cancer. When taking oral contraceptives or taking them in the past few years, estrogens may slightly increase the risk of breast cancer.
A small increased risk of breast cancer is also associated with the estrogen and progestin given to women during menopause (hormone therapy).
The drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) increases the risk of breast cancer in both women who take it and their daughters. It has also been shown to increase the risk of cervical and vaginal cancer in the daughters of those who took the drug. Treatment of breast cancer with tamoxifen increases the risk of endometrial cancer.
Male hormones (androgens) such as testosterone or danazol can cause liver cancer if taken for a long time.
People who have received chemotherapy (alkylating agents) and radiation therapy for cancer may develop a second cancer years later.
infections
Various viruses are known to cause cancer. In addition to causing genital warts, HPV also causes cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, penile cancer, and anal cancer in men. HPV also causes some types of mouth and throat cancer.
It is possible to develop liver cancer after being infected with the hepatitis B or C virus.
Cancers of the blood system, such as lymphomas, are caused by some human retroviruses.
There are also bacteria that can cause cancer. Stomach cancer and lymphomas can be caused by Helicobacter pylori, which causes stomach ulcers.
Some parasites can cause cancer. Schistosoma haematobium infections can cause chronic inflammation, scarring, and bladder cancer. Cancers of the bile ducts and pancreas can be caused by a parasite called Clonorchis sinensis.
Inflammatory disorders
Cancer is often associated with inflammatory disorders. It can lead to colon cancer and bile duct cancer if ulcerative colitis is not treated.
Crohn’s disease can also lead to colon cancer.
Keep reading about cancer and other diseases at EMC: